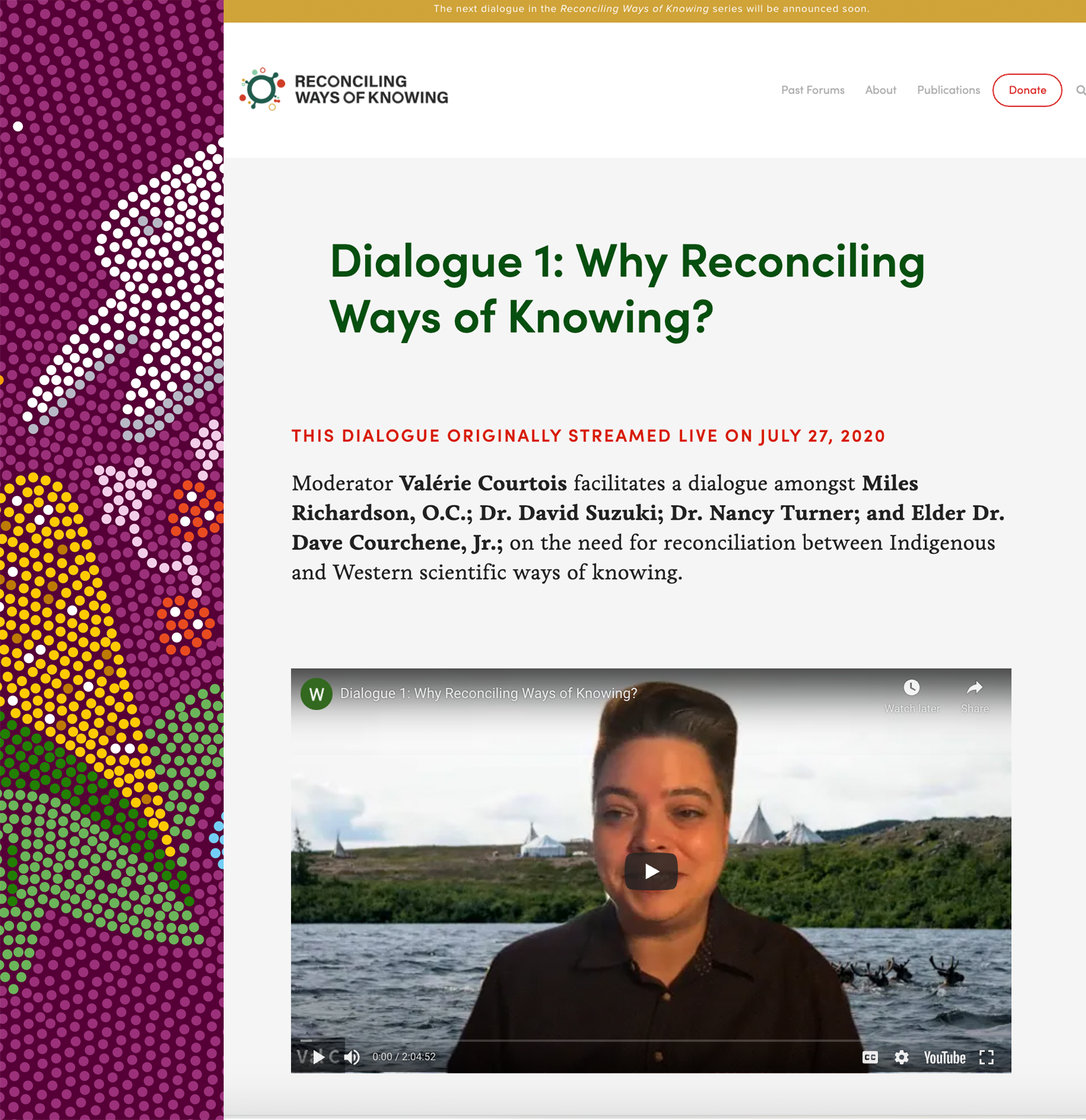
Source: Carol Zavaleta-Cortijo, James D Ford, Ingrid Arotoma-Rojas, Shuaib Lwasa, Guillermo Lancha-Rucoba, Patricia J García
Year: 2020
“Indigenous populations are at especially high risk from COVID-19 because of factors such discrimination, social exclusion, land dispossession, and a high prevalence of forms of malnutrition. Climate change is compounding many of these causes of health inequities, undermining coping mechanisms that are traditionally used to manage extreme events such as pandemics, and disrupting food systems and local diets. Addressing underlying structural inequities and strengthening Indigenous knowledge systems offer opportunities for building resilience to compound socioecological shocks, including climate effects and pandemics.”